Qualities and attributes of an occupational health and safety practitioner
Qualities and attributes of an occupational health and safety practitioner
It is legal requirement in almost all countries
that organizations (considering the number of employees/workers) must have
access to appropriate competent people to give them health and safety advice.
These safety specialists or "safety practitioners" may work within
the organization or may be brought in from outside as consultant. They are
responsible for giving correct advice to the organization so that the
organization can comply its legal obligations and achieve its policy objective
& targets.
Roles and responsibilities of health and safety practitioner
Providing advice and guidance in implementation of
Safety Management System & health and safety standards.
Promoting a positive health and safety culture in
organization to achieve the target of zero incidents
Advising management on accident prevention, accident
reporting and investigations to decide the controls and to prevent the
recurrences.
Advise management for developing and implementing
policy for establishing positive safety culture.
Directing the development of adequate risk
assessments and managing the risk at ALARP.
Help management to identify the training needs
based on training need identification. Also guiding for planning the training
schedule and development of training modules.
Monitoring health and safety performance through leading and lagging indicators and highlighting the area for concerns for
continual improvement.
Other than above, He must guide management to
maintain below health and safety records
- PPEs issue register.
- Record of statutory training and skill development.
- Record of workers competency.
- Record of workers health and safety violation and disciplinary actions.
- Record of workers medical fitness and periodic medical check.
- Record of Hazard and risk assessment and communication to workers, etc
Occupational Health and Safety practitioner’s competency
Safety practitioners must be qualified and
experienced in health and safety. Below framework of his competency is
suggested.
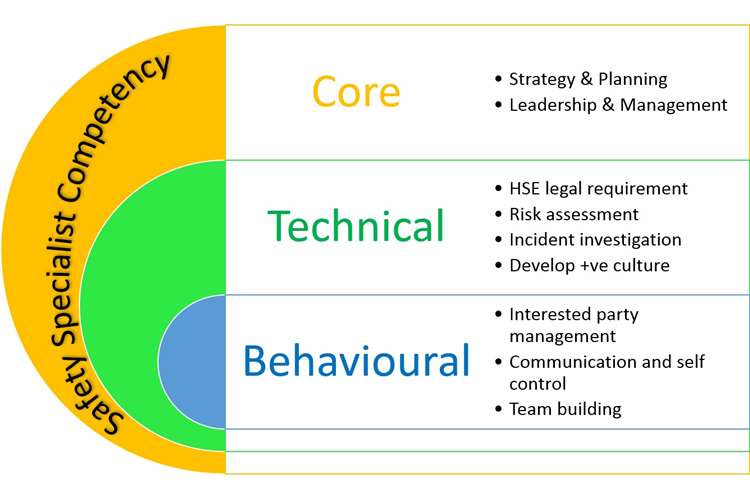 |
| Occupational Health and Safety practitioner’s competency |
Qualities and attributes of a safety practitioner
Safety practitioner should be a good Leader
The Safety practitioner must be a good leader in
meeting organizational health and safety requirements by leading and
implementing the operational plan. He must motivate the workforce by sharing
his knowledge on health and safety issues and managing risks in the workplace.
He must advise management on the efficient use of resources in order to develop
a positive safety culture and prevent incidents. He must act as a leader and
set an example by following a safety commitment to workers, employees and
managers. He should be open to advise people on safety issues and help them
decide on controls to eliminate the hazards.
Be a role model for others to be inspired by you.
Develop discipline yourself. Take responsibility for your actions. Work with
determination and passion.
He must be visible and demonstrate confidence to
influence the workforce by providing quick feedback on all safety related
issues, ie a substandard act and substandard conditions can really have an
impact on organizational performance. He needs to make frequent site visits to
the workplace and connect with people to build a great relationship with them,
which will build trust between the two.
The Safety practitioner should be a good listener
to manage conflicts and especially as a leader to encourage formal discussion,
rather than providing a quick and ineffective response, which can motivate the
people in the workplace and will provide an opportunity immediate to work on
ambiguities. He must collect comments from people in the workplace to understand
the real risk and the difficulties in deciding on control over hazards, then
assess the situation to advise correctly. He must be dominant in meetings but
be respectful because he must deal with many peoples at all levels.
The safety practitioner should assist management in
identifying the health and safety goals and associated resources required,
including procedures and practices for achieving them within the time frame. He
must advise the management and the people in the workplace for development of management
programs to achieve the objective and the targets set.
He must monitor changes in the installation
(equipment, chemical, process, technology, administrative, etc.) and assess the
impact on current risk management. All changes must be ensured to be
communicated to the people likely to be affected by these changes by ensuring
the implementation of the change management procedure.
Safety practitioner must be strategic and a good planner
The safety practitioner must establish priorities
in accordance with the health and safety management policy, objectives and
targets to ensure the effective implementation of the controls decided in the
risk assessment. It must promote innovation in the field of Health and safety
for a sustainable business and enhance the brand of the organization. He must
advise management to identify and maintain good relationships with internal and
external stakeholders in order to build a good reputation in the market. He
must build and maintain the positive relationship with the statutory and
regulatory bodies for the benefit of the company. This will assist management
in effectively complying with all legal, statutory and other health and safety
requirements.
By giving correct technical recommendations, he can
build a good reputation with superiors or managers, then everyone will trust
him, this will certainly contribute to developing a positive safety culture in
an organization. Be legitimate on good safety suggestions, it should be
practical and profitable because most managers understand the language, that is
financial language. Present any safety suggestions or recommendations in
financial terms so that management can easily understand and convince that
implementing these safety suggestions is cost effective and helps increase
revenue.
So, summarizing all the above, financial language
is very important in convincing senior management. As a rule, management and
line managers understand only one language, viz. financial language. To change
the priority, safety recommendations / communications can be presented in terms
of cost-effectiveness. Connect each threat to safety with financial
implications and present it to management. Safety recommendations can be
presented along with a cost comparison. this applies to both the positive and
the negative. What will be the financial loss if you do not take corrective
action regarding a unsafe act and unsafe conditions? What would be the
financial benefits to the business if we took corrective action against unsafe
practices. When considering high potential near misses or any unwanted
incidents, compare losses to investment. Indirect losses must be presented in
terms of tangible financial costs.
The safety practitioner must be able to influence
senior management to fulfill their commitment to safety, if safety is not a real
priority for them, otherwise accidents and incidents are not preventable.
Safety practitioner must have sound knowledge on legal requirements
The health and safety practitioner should advise
management on legal matters, so they should be fully aware of this and be able
to interpret it correctly. Without having a good knowledge of HSE legal
standards, he cannot guide management for the development of a health and
safety policy consistent with the corporate strategy and culture.
He must be able to develop a legal register which
guides the management to develop a positive culture in an organization and
helps to comply effectively with all the legal obligations applicable for a
sustainable business. The safety practitioner should be a good auditor /
proficient to monitor the health of the legal compliance management system,
this will help manage any threat to the business.
Safety practitioner must be expert in OHS risk management
There can be a threat to businesses regarding non-compliance
with legal obligations, operational risks, hidden internal and external risks,
on-site and off-site emergencies and any unexpected changes in the
organizational structure. Therefore, the safety professional must be proactive
in identifying and acting on these business threats related to safety issues.
There are several methods available around the
world for hazard identification and risk assessment, but the safety specialist
must be able to identify the right one for their business. He must be an expert
in risk prioritization and suggest to the management profitable controls to
minimize the risk at ALRP level.
As the risk register is a dynamic document, the
safety specialist must monitor its relevance and review and update timely with
any change in operation, installation, technical changes or administrative
changes. He must be able to escalate unforeseen risks for management with
appropriate corrective actions based on a systematic analysis of the data.
Safety practitioner must be expert in incident investigation
The Safety specialist must be able to develop and
implement the robust incident reporting and investigation procedure. It must be
a management procedure because it applies to all the disciplines of the
organization. There are several techniques available in the world for the
investigation of incidents, but the safety specialty must decide which
technique is most appropriate for its organization. He must be able to identify
direct and indirect losses related to each incident and be able to present
appropriate effective corrective measures to management in a cost-effective
manner. He must have good relations with regulatory bodies to help the
organization to report the major accident and any dangerous occurrences. He
should be able to develop and implement an emergency management and response
plan.
Safety practitioner must able to develop the positive safety culture
Safety is parallel to the operation of the company;
it must be able to work in a transversal way to support the productivity of the
company and ensure health and safety too. He must understand workers'
perceptions and help management identify the criteria for competency in
selecting the right contractors. He should be able to identify basic employees
and workers' welfare facilities, viz. potable water, chek and change room, rest
room, washroom, drinking water, dining room, decontamination room, toilet, etc.
He must educate workers on their well-being and maintain hygiene in order to
prevent occupational diseases and control other physical risks. He must be able
to develop and implement the criteria of competence of contract workers,
develop modules to identify training needs and training modules. He must be
proactive in identifying any developments in new legislation, technology, etc.
which could affect business risk management and should recommend the latest
requirement, effective changes to the health and safety management system and
risk control strategies.
Safety specialist must able to manage the interested parties
He must be able to identify all the appropriate
organizational stakeholders and gather the needs and expectations for better
management planning by creating a strong network. Provide training and educate
staff on the organization's safety management system, including safe work
practices, policies and procedures. If necessary, he has to stop work for a
while, if it seems dangerous and must rigid to his decision till correction.
He must always be proactive and not reactive. He must investigate incidents to
find out the root causes and not promote the concept of fault finding.
To provide training and engage the workforce, he
must be confident and expert in the subject of training. He must be a trusted
adviser for internal and external parties. He must be able to manage the moral,
ethical and social status of the organization and advise management in a
cost-effective manner to improve the overall safety management system.
Safety specialist must be good communicator and manage self-control
He must develop effective two-way communications by
organizing HSE meetings, toolbox discussions, safety training, a safety
suggestion program, etc. because mostly, the main causes of accidents are due
to lack of training, awareness of dangers and complacency. He must use all
possible means of communication to educate staff and set up feedback
management. He must develop the employee motivation scheme and ensure the
participation and consultation of all employees, workers, etc.in risk
assessment and any other change management.
He must manage his strength, his weakness and
always update his knowledge on the latest technical health and safety issues
and good practices from similar types of industries / businesses. He must be a
good listener and always thinking out of the box to maintain a successful
engagement with all interested parties. Be able to better anticipate the future
of the business strategy to define health and safety management programs. His
vision must be clear, which helps motivate and align his team to achieve the
common organizational goal.
Safety specialist must be good team builder
He must feed and inspire his team, take
responsibility for the outcomes. Accept blame for the team result and always
give credit to others if successful. Act as a good mentor to develop supervisors
on risk assessment, decide on hazard controls, hazard identification, change
management, development of critical process procedures, etc.
He must demonstrate good teamwork by appreciating
the achievements, by showing interest in all the good suggestions from the
workplaces and by strengthening people's morale to develop a culture of safety.
Conclusion
Health and safety officer/specialist must be
competent and expert in HSE legal requirement, Risk assessment techniques and
risk management, incident investigation, interested parties management and he
must develop positive safety culture in an organization by using his expertise
communication and self-control and ability of team building skill.
Related Articles









No comments
Please don't add links in the comments, they will be treated as spam comments