Safe Mechanical completion, Pre-commissioning, Commissioning and startup | Oil & Gas facility
 |
| Safe Mechanical completion, Pre-commissioning, Commissioning and startup | Oil & Gas facility |
Safe Mechanical completion, Pre-commissioning, Commissioning and startup | Oil & Gas facility
This article provides the systematic
approach for commissioning and startup of any new facility, mainly for
brownfield.
Meaning of
commissioning: Commissioning is the phase in a
project when design process fluid or safe fluid is introduced to the systems and
sub-systems. In simple word, project construction work is over and special activities
started to validate that the equipment, machines, systems and subsystems, other
system components are installed, tested and operated in line with project requirement
or intent.
For safe, swift and successful plant
commissioning, activities are divided into 12 key elements based on any project
philosophy.
- Review and updating of Project HSE plan
- Review of project Risk register
- Planning of commissioning process
- Mechanical completion
- Examination of P&ID
- Pre-Commissioning of system, component or equipment
- Commissioning
- Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR)
- Plant Startup
- Initial operation
- Performance test for validating plant intend
- Post commissioning
1. Review and updating of Project HSE plan
HSE Plan provides a document to
cover the project Health, Safety & Environment management system and contractor
must implement during the execution of the project as per agreed conditions. This
is dynamic document and must be reviewed at various phases of project right
from construction phase to commissioning, startup and operation.
2. Review of
project Risk register
Risk register provides the assurance
to project team that they have identified all the work-related hazards and risk
is managed at ALARP level. This document is continuously reviewed and revised
at each phase of project. Before planning the commissioning phase, Risk register
must be revised by identifying the new hazards, analyzing the existing controls
and assessing the risk. It also provides the information about any further
requirement of safe work practices and work procedures.
3. Planning of
commissioning process
Planning is the first element to
commission of any facility safely and in time. Here clear organizational chart with
roles and responsibilities of all members of commissioning team are framed out.
Decide all different types of checklists i.e. structure, piping, mechanical,
electrical, instrumentation, etc and develop operating manual. Other important
procedures are;
 |
| Planning of commissioning process |
- Pre-commissioning procedures viz. air blowing, water flushing, steam blowing,
- Commissioning procedures for the systems and units.
- Safety procedures
- Quality control procedures
- Security procedures
- Emergency management plan and Response procedures
Other than above procedures,
Commissioning status progress reports need to be developed to measure
commissioning progress. Test records need to be maintained to keep track of all
pre commissioning and commissioning activities. Develop a punch list format
with a construction department together. Planning of manpower requirement
including the pre-commissioning team, the commissioning team, the operating
team and the maintenance team.
Planning must be done along with client
so that their team should join the commissioning activities on site (Involvement
of client engineers/ operators is very important as this is the best opportunity
to trained them.). Other agencies may be involved as contractors’ vendors and
process engineers.
Ensure advance planning of material
requirement. Material like blinds, split pieces, hoses, steam blowing equipment,
tool box/ kit, etc my requires during pre-commissioning and commissioning
activities.
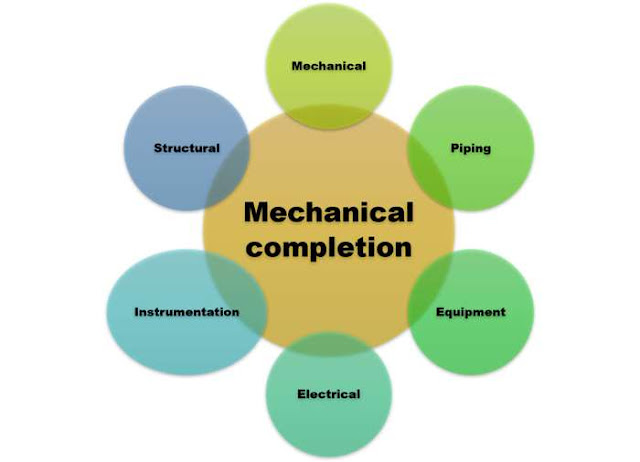
4. Mechanical
completion
Mechanical completion means
construction completion and here mainly the construction team is involved but
some time commissioning team may be involved for better understanding. In Mechanical
completion phase all machines, all equipment and site construction are inspected
and tested to validate that the installation is in line with approved drawings,
specifications and ready for pre-commissioning or commissioning in safe manner.
It also confirms the compliance of project requirement.
As in project, different disciplines
are working and therefore mechanical completion may be separated by different disciplines
viz. Mechanical, Piping, Electrical, Instrumentation, Automation, Structural
integrity, etc.
- Nameplate, display details at tanks, vessels, rotating equipment and other machines.
- Internal inspection of tanks and vessels
- Hydro-static tests of vessels and tanks
- Dimension control
- Bolt tension
- Preservation
Vendor representative must be on
site for complicated machines viz. compressors, blowers, pumps.
2)
Piping Discipline: Validation
for completion and correction of
- NDT
- Pipe supports
- Confirm that damages during flushing, cleaning and pressure testing are rectified
- Blowing/ flushing finished
- Chemical cleaning & drying
- Preservation
- Reinstatement
- Bolt tension
- Insulation on piping except on flanges and flow coding.
3)
Electrical Discipline: Validation
for completion and correction of
- Electrical panels installation
- Cable trays and its supports
- Cabling in tray and cable dressing
- Bend radius of the cables
- Connection/ Termination
- Grounding
- Megger testing
4)
Instrumentation Discipline: Validation for completion and correction of
- Instrument panel installation
- Cable trays and its supports
- Cabling in tray and cable dressing
- Bend radius of the cables
- Connection/ Termination
- Grounding
- Instruments
- MOVs
- loop checks
- Tightness test & flushing of tubing
5)
Automation Discipline: Validation for completion and correction of
- DCS console and its user-friendly installation
- Central process unit
- Cabling & tagging
- Termination
- Grounding
- Loop checking
6)
Structural Discipline:
Inspection of all supporting structures for
- Dimensions
- Integrity
- Bolt tension
5. Examination
of P&IDs
Commissioning engineers are
examining the P&ID to validate the system for engineering and construction
error after handing over of system or system from construction to commissioning
team, here punch points are submitted for rectification.
To perform this stage, ensure latest
revision of P&IDs marked with system boundaries, equipment drawings/
datasheet, different type of checklists, national and international standards, hookup
drawings and vendor documents for complicated equipment.
Below items should be checked during
P&ID examination.
- All piping, fittings and valves
- All equipment and machines ie. Motors, pumps, vessels, exchanges, heaters, turbines, compressor, etc along with vendor representative.
- All instrumentation including nameplate, flow direction, mounting position, temperature range, pressure range, flow and other measurement range.
- Safety consideration i.e. Whether it is safe installation and Support safe operation too.
- Operational convenience i.e. Requirement of platform or other safe approach.
- Maintenance convenience i.e. requirement of monorail/ hoist over motors and pumps.
During P&IDs examination, some additional
activities may be carried out like provision of temporary identification tags
& signs for piping, valves, machines and equipment.
Any deviations in this process must
be marked in punch point list, signed it and submit to construction team and QA/QC
engineers. After correction of punch items and confirmation from construction
and QA/QC department, joint visit should be done to validate the compliances
and closed immediately by signing off.
6. Pre-Commissioning
of system, component or equipment
After finished of mechanical
completion i.e. construction completion, Pre-commissioning activities starts to
validate the equipment or component is fabricated, installed, cleaned and
tested in accordance with a design intend and ready for commissioning. Pre-commissioning
activities includes energizing of equipment/ machines, flushing and cleaning,
drying, leak testing, running of equipment, running of electrical motors, loading
of catalyst in reactor, loading of catalyst in columns, dry run, etc. sometimes
pre-commissioning activities are included into mechanical completion.
It also ensures the closing of columns,
vessels, drums, tanks, final restoration of systems or subsystems after cleaning,
air tightness or leak testing of systems, lubricants application, etc.
Sometimes pre-commissioning includes
installation of filters, packing of distillation columns, molecular sieve beds,
refractory dry out, instrument/ electrical and motor loop testing etc. All the
findings/deviations must be noted in punch list.
 |
| Pre-commissioning |
- Procedure for necessary spectacular blind installation
- Procedure for field non-return valve internal installation
- Procedure for checking refractory lining installation and checking of mechanical interlock.
- Procedure for checking of distillation or scrubbing columns packing.
- Procedure for catalyst loading in reactor with installation of filter
- Procedure for air blowing, steam blowing, etc.
- Procedure for water flushing
- Procedure for chemical cleaning
- Procedure for tightness test
- Procedure for cooling water
- Procedure for mechanical test run of pumps, etc
Below sequence is recommended
for pre-commissioning activities based on its priorities.
- Power and control system i.e. electrical substations, Building power, etc
- DCS and PLC systems and instrumentation
- Row water and firefighting systems
- Wastewater treatment systems
- Oil, cleaning & chemical sewer systems and neutralization pits
- Service water, potable water and cooling water systems
- Instrument air, plant air and air regeneration systems
- Water treatment systems.
- De-mineralisation plant
- Boiler water system
- The nitrogen system
- Flare system
- Plant safety equipment and fire and gas detection
- Fuel gas and fuel oil system
- Slop systems
- Flushing oil system
- Boiler systems with steam and condensate networks
- Aromatics and caustic drain systems
- Feed and product storage systems
- Product and feed systems
- Amine treatment section
- All the process systems, etc
Pre-commissioning checklists must be
developed for different types of machines, equipment and systems to record the result
of inspection and to confirm readiness for commissioning. All these checklists
should be witnessed by the client, Project Management Control (PMC) , the licencor,
etc. Test records must be maintained for
all system checking, preparation activities and other number of tasks like chemical
cleaning, drying, air tightness test, loading of catalyst, blind list status
and the performance indicators. Similarly, records for QA/QC documentation, system
punch list associated with various pre-commissioning activities viz piping, stationary
equipment, rotating equipment, instrumentation pre-commissioning activities and
tightness tests should be maintained. This will help to track the planned vs completion
and the remaining tasks which must be done. Status of the punch list report for
outstanding punch points must be monitored.
Vendor specialists should be on site
for major items of rotating machinery, major utility systems, special
electrical & instrument control equipment, package units which have been
assembled by someone at site shipped by a vendor, the licensor do the final
inspection of critical equipment installation as well as the supervision of catalyst and chemical loading.
After completing the Pre-commissioning
check with validating all punch points, facility will be ready for
commissioning.
7. Commissioning
In a project, after
pre-commissioning, next phase is commissioning where design process fluids or
safe fluid are introduced to the systems and subsystems. Commissioning is the stage where project finished
its construction phase and planned to entire in commercial operation stage. In
this stage, it is validated that each system or subsystem is fabricated,
installed, cleaned and tested as per design intend and the systems are ready for
startup. Some time it is called as cold and hot commissioning. Cold commissioning is of two type i.e. dry
commissioning and wet commissioning.
 |
| Types of Commissioning |
- Dry commissioning: means tests and procedures that are conducted without solvents or process fluids. Eg. interlock and emergency shutdown tests or control system sequence checks, etc
- Wet commissioning: means water/ safe fluid or a solvent has been introduced into the systems or subsystems for testing purpose to simulate the operating scenarios to understand the system's behavior. Eg. running of pumps in closed loops or interlock and emergency shutdown tests.
- Hot commissioning: means design process fluids are introduced to the systems and subsystems and the activity is similar to wet commissioning activities like running pumps with a closed loop.
For safe commissioning of facility,
ensure safety measures like permit to work system. If the new facility is adjacent to existing
one and employees/ operators would be same, then existing PTW should be used
otherwise it should be modified adequately.
Construction area might be fenced to
separate it from existing operational facility then security and access control
must be ensured. Emergency response procedures must be made aware to all
commissioning team and other related workforce. Final leak testing, final drying,
final purging and energizing must be completed in safe manner. For initiating
systems and subsystems filling with process media, operation of systems and
subsystems, completion of system, etc lot of documentation is required in commissioning
phase. Therefore, commissioning sequence must be followed for commissioning
of the facilities system by system and unit-by-unit basis and it
should be backwards approach. Below
backward sequence is suggested;
- Control systems DCS /PLC
- Utilities i.e. air, nitrogen, water, steam etc.
- Product storage tank systems
- Loading systems
- Process units ie. reactor, furnace, exchangers, vessels, columns, etc
- Raw material feeds
- Raw materials storage, etc
For safe commissioning, whatever commissioning
procedures finalized in planning stage, these all procedures must be
followed. Eg.
- Commissioning procedures for utilities and services
- Commissioning procedure for uses of water or a solvent in each system
- Commissioning procedure for introducing process fluid in each system
- Procedure for Interfacing (operation and maintenance work with commissioning work)
- Product quality control procedure
- Procedure for laboratory analyzes for the new facilities
- Procedure for production planning.
on operation of the new facilities
must be integrated during the commissioning startup and initial operation phase
this commences with first requirements for fuel gas and other things from the
existing plant for boilers startup and dry out through initial feed stock
transfer and final product storage blending and shipping.
maintenance support must be ensured
by company to monitor pump temperature and vibration during commissioning. All
commissioning activities by contractors, vendor specialists, etc must be carried
out under the supervision of commissioning team and the licensor. Process
licensor may supervise the commissioning activities for important and critical systems
and must provide technical assistance during all stages of commissioning. Process
operating parameters and conditions will be advised by process licenses,
process engineers.
8. Pre-Startup
Safety Review (PSSR)
The purpose
of Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR) is to ensure that new/modified facility is
ready for safe and continuous operation. The PSSR must confirm the following,
prior to the introduction of process fluids to a process/systems/subsystem.
- Construction and equipment meet design specifications.
- Safety, operation, maintenance and emergency procedures are present and adequate.
- For new/modified facilities, a MOC procedure had been followed, and all HAZOP recommendations have been implemented before startup.
- Training of each employees involved in operating a process has been completed.
PSSR is the last step in commissioning
process and managed by commissioning manager and the client commissioning team
jointly. Vendors and licensor may join
PSSR. Completion of PSSR and compliance of all its punch points will validate
the facility/system for its readiness and to commence safe startup.
9. Plant
Startup
Plant startup is the phase where the
entire plant, all systems and subsystems are taken into operation, process
fluids are introduced, and process conditions are established with intent of
making products. For continuous startup
activities, employees must be assigned in work shift duties so that client, the
contractor and some vendors and licensor should be available 24x7. Shift
logbook with clear instructions for its filling should be specified before starting
the plant.
Once again assure the compliance of
punch points of PSSR and ensure the pre-startup checklist by tick mark on it
step by step. Checks are;
- Whether all utilities available for safe startup
- Whether feed is available
- Whether enough product storage available
- Whether all involved startup team
members are well aware about different startup procedures
- Pipe and equipment purging procedure
- Pipe and equipment evacuation procedure
- Procedure for Initial introduction of feed and chemicals
- Procedure for initial heating or cooling
- Procedure for loading catalyst or other media into initial conditions
- Startup sequence with normal operating data
- Procedure for plant operating under normal conditions
- Procedures for shutdown
- Procedures for emergency shutdown
- Procedure for simultaneous operation
Ensure implementation of proper interfaces,
i.e. operations and maintenance, product quality control by company with
quality control laboratory analyzes, production planning by company and emergency
response for contractors, security and safety together by company and
contractor. Similarly, maintenance support by the company and on duty technical
support managed by the contractor and the licensure. Where required, the
process licensor supervise the start-up of relevant systems and provide technical
assistance. Process operating parameters and conditions will be advised by
process licensor and process engineers.
All process parameters and data must
be maintained which would be most useful for next phase i.e initial operation
phase. After finished of successful
startup, plant is ready for initial operation.
10. Initial
operation
Initial operation means the entire
plant is running in continuous operation, fine-tuned and prepared for the
performance test. Most important things are
fine tuning of control loops, complete process and testing of operational
limits. Check the limit that the emergency shutdown starts and observe that
emergency shutdown is working well. Maintain all important data related to equipment,
relevant processed data and as well performance data. This will help for next
stage i.e. performance tests.
Still successful completion of
initial operation stage, licensor involvement may be there as per requirement for
relevant systems to provide technical assistance and may advise for process
operating parameters and conditions.
11. Performance
test for validating plant intend
Performance testing validates the
plant that it is operating according to design intend. Performance testing includes
facility operation and performing numbers of specified activities,
demonstrations and tests to measure the new plant and equipment against the approved
project design and specified parameters.
Time duration for performance test
is varies from plant to plant and as well type of industry to industry. A simple water treatment plant may finish a
performance test within a 24 hours’ time period or 48 or 72 hours but other
large plants or complicated plants like oil refining units with numbers of trains
may takes a month or several months because each trains will be run step by
step then all trains should be run simultaneously/ together. Shift duties must
be assured for continuous monitoring and observing the performance trend. If at
certain period, performance test gets fail, then licenser intervention is
required. It is good practice to have/
maintain separate logbook by the client and the contractor and to tally with
each other to detect any error. Performance tests procedures must be ensured by
both the party and follow the same agreed sequence.
During
performance test below activity should be ensured by
both client and contractor;
- Quality control
- Production planning
- Emergency response
- Security and safety together
- Maintenance and technical support
- Supervision and monitoring of process parameter.
- Recording of all readings
- Install an additional measurement device if existing is not adequate.
- Comparison of process data with specifications
- Maintain shift book
- Monitor the DCS system
- Sampling of products and lab analysis
- Analysis and assessment of performance test parameters
If all performance parameters are
matching with project intended parameters, then we will have a final acceptance.
Generally, performance test data requires about two to three weeks for evaluation
by the client contractors and the licenser. If it is satisfactory then final acceptance i.e.
cares, and custody is transferred from contractor to the client and this is
called as project plant hand over. Satisfactory result of performance test may result
to official handover of the plant and proves that commissioning team has
fulfilled the obligations. But there may be minor punch list which is to be
attached with final acceptance certificate.
12. Post
commissioning
Post commissioning is the phase
after handing over of plant to the client. Handing over to client means final
acceptance certificate is now signed by client and operations assistance is not
needed anymore. Outstanding punch points are solved, and some adjustments,
modifications and fault corrections being completed. Also, some routine
maintenance checks and performance findings being evaluated and monitored for process
equipment and items covered under warranty. Problems and operating data is being
collected and evaluated to ensure consistent plant operations. Here contractor
commissioning team who was involved in commissioning process will stay and responsible
for solving the outstanding punch points and solving any troubleshooting. As
this commissioning peoples are having experience of this particular plant, they
know everything, where to go for which particular problem, what will be
solution for particular deviations, etc. After few weeks or months as per
project agreement, one or two persons may stay along with client and they will
be responsible and coordinate for production planning, operations, maintenance,
product quality control, emergency response, etc. Licensor may also stay there
as per project agreement for technical guidance on process parameters.
Conclusion:
Safe commissioning of any new
facility or modified facility can be achieved successfully by proper commissioning
planning, well organized team framework, proper coordination between client,
contractor, vendors and licensor, ensuring availability of Manual and procedures,
security and safety system, well developed data entry formats and checklists,
logbook and other records, etc. Compliance of Safety management system and proper
coordination between different disciplines are the key areas for safe and successful
commissioning of project, where operational facility is adjacent to new project.
Related Articles
You may find affiliate
links in this article. This means that if you click on a link and purchase any
of the products on this page, we may receive a commission, at no additional
cost to you, It does not affect our knowledge sharing, opinions or reviews. Everything
we do is benefit for you as the reader, so all our knowledge sharing, reviews
are as honest and unbiased as possible.





I think this article will fully complement you. Please continue publishing helpful topics like this. Regards, from Asset Management Software
ReplyDeleteAged Care CMMS Software
Pre-Start Checklist
Thanks you for appreciation
ReplyDeleteThis is so useful, very detailed! well done!
ReplyDeleteThanks
DeleteVery useful guidance. Weldone.
ReplyDeleteThanks for appreciation
DeleteVery useful document.
ReplyDeleteThanks for appreciation
DeleteExcellent, simple, clear and very detailed.
ReplyDeleteA job very well done !
Regards,
excellent and well explained
ReplyDelete