Occupational ill-health | Prevention and Management of occupational diseases
Occupational ill-health | Prevention and management of occupational diseases
Occupational ill-health is recognizable,
undesirable physical or mental condition occurring by a work-related activity
or conditions and may become severe overtime. It is a chronic disease caused by repeated
exposure to work hazard during performing routine work activities. It has multiple causes including work environment together with other risk
factors.
Occupation diseases may be occurring individually or among a group of exposed people
and develops over time. Before
identifying, the illness may need substantial treatment or could be permanent.
Type of Occupational Diseases/ ill-health
Occupational health hazards are due to exposure of
chemical, physical, biological or ergonomic.
Occupational diseases are broadly divided into two
categories
- Disease caused by exposure to agent
- Diseases by target organ
Occupational Diseases Caused by Exposure to agents
1. Caused by exposure to chemical agent
2. Caused by exposure to physical agent
- noise, vibration, compressed air
- ionizing radiation, Eg. -X- rays, gamma rays, beta particles, alpha particles
- non-ionizing radiation Eg. Microwaves, infrared, visible and UV light (optical)
- Exposure to extreme temperature and humidity.
- Ergonomic exposure Eg. Repeated movement, body posture, load bearing, etc
3. Caused by exposure to biological agent
- Infectious Eg. Bacteria (Tuberculosis, Leptospira, Tuberculosis, etc), Viruses (Hepatitis B, etc)
- Parasitic diseases
- Allergens of biological origin Eg. laboratory animals, insects, mice, wood and other plant material, fungal spores.
4. Caused by Psychological exposure
Various
aspects of work activities, peer group pressure, and work environment and work organization
may be stressors.
[What is occupational health?]
Occupational Diseases by target organ systems
Respiratory diseases/ Inhalation disorders
Respiratory system is split into three areas
- Upper respiratory tract or airways, including the mouth, nose, sinuses, throat and larynx
- Middle respiratory tract, including the windpipe and bronchi
- Lower airways, including bronchioles and lung vesicles.
Inhalation disorders are associated with inhaling
a chemical or biological substance that may be in the form of dust, smoke, fog,
gas or vapor or animal allergens, fungal spores and bacteria. When workers
breathe them in, they can damage the lungs and other parts of the respiratory
tract. In some cases, dangerous agents travel from the lungs to other parts of
the body and damage other organs.
Many people have a genetic predisposition to
allergic diseases. After exposure to chemical or biological agents, they are
more likely to develop conditions such as rhinitis and asthma.
Types of inhalation problems | Lung Diseases
Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis includes a group of lung diseases
caused by the inhalation of insoluble dust, usually mineral dust, that the
lungs cannot eliminate. The most common diseases in this group are
- Silicosis,
- Juvenile pneumoconiosis
- Asbestosis.
Silicosis:
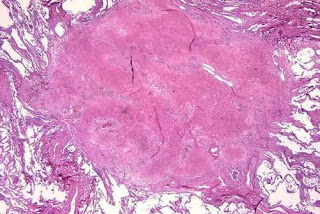 |
| Occupation disease - Silicosis |
It is form of pneumoconiosis, a
"progressive" disease, worsens even after exposure stops, and is
characterized by increased respiratory difficulties, which sometimes result in
death. Allowable exposure limit for respirable crystalline silica is 50 µgm per
cubic meter of air.
Cause: Inhalation of crystalline silica
dust (quartz).
Source of exposure: It is
common among people working in quarries, mines and sandblasting, as well as
among people who work in the ceramics industry and iron and steel foundries.
Preventive measures:
Ensure adequate exhaust/ ventilation, use frequent
water spray to reduce emission. Give frequent break, limit manual operation or
limit the manpower, ensure use of respirators at worksite.
Juvenile pneumoconiosis:
It is form of pneumoconiosis and
characterized by a mild cough and the production of black sputum. In some
people, this leads to progressive massive fibrosis, disability and death.
Cause: Inhalation of coal dust.
Source of exposure: Coal
mine, coal transportation, coal handling
Preventive measures: ensure
use of dust mask, Shower after duty, decontaminate the clothing/ apron, remove
the dust safely from clothing, before eating and drinking wash face and hands
thoroughly, no smoking at work area
without washing hand, report immediately about any symptoms of pneumoconiosis
to physician, carry out periodic medical check-up & regular chest X-rays.
Asbestosis:
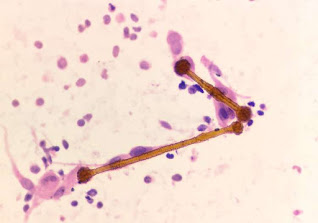 |
| Occupational diseases - Asbestosis |
Cause: Inhalation of asbestos fibers
Source of exposure: Asbestos manufacturing
mill, asbestos handling, equipment manufacturing, insulation work, other
asbestos handling work.
Preventive measures:
- Make sure the work area is isolated from the rest facility.
- Air conditioning should be turned off.
- Apply a wetting agent to asbestos material to minimize the release of fibers into the air.
- Cleaning should be done with damp mops, rags and sponges. Do not allow the use of common vacuum cleaners. Asbestos fibers can pass through the filter of common vacuum cleaners and reach the air. However, HEPA (high efficiency particulate air) vacuum cleaners can be used. Make sure all asbestos materials, disposable equipment and clothing are placed in sealed and marked containers and disposed of properly.
Work-related Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
It
is a lung disease caused by narrow airways, which makes breathing difficult.
Other symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath and increased phlegm
production. Conditions in which the air flow in the lungs is gradually reduced
by damage to the lung tissue and respiratory tract.
Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a term used to describe a progressive
and irreversible limitation of air flow to the lungs. COPD includes two main
diseases: chronic bronchitis bron: a condition in which inflammation narrows
the airways in the lungs (bronchi) and causes chronic bronchial secretions; and
Emphysema: a permanent destructive bond
Cause:
smoking, exposure to different types of
hazardous substances, occupational exposure to various dusts, fumes and vapors,
etc.
Source of exposure: : Dust, gases and fumes of
professional origin, air pollution in the environment.
Preventive measures:
- Reduction of total personal exposure to tobacco smoke, dust and workplace chemicals and indoor and outdoor air pollutants.
- Brief treatment for tobacco dependence is effective
- Three types of counseling are particularly effective: practical advice, social support during treatment and social support organized outside of treatment
- Chronic treatment with systemic glucocorticosteroids should be avoided due to an unfavorable risk / benefit ratio.
- All COPD patients benefit from physical training programs, improving both exercise tolerance and symptoms of dyspnea and fatigue.
Non-malignant pleural disease
Non-malignant
pleural disease is a non-cancerous condition that affects the outer lining of
the lung (the pleura). It includes two forms of disease: diffuse pleural
thickening and less severe pleural plaques.
Other Respiratory Diseases
Rhinitis Allergic
Allergic Rhinitis is the inflammation of the cells
along the nose, is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal airways
produced by an allergic reaction. When caused by plant pollen it is typically
referred to as hay fever, but it may be caused by a wide range of other
substances that can be present in workplaces. Often, these are substances that
can also lead to occupational asthma. Allergic rhinitis is often characterised
by common cold-like symptoms, but without a fever, congestion, itching and
sneezing.
Cause: Inhalation of plant pollen, grass pollen, dust
mites, animal dander, which is old skin, cat saliva, mold,
etc
Preventive measures:
- if you’re sensitive to tree pollen in the spring, you may want to start taking antihistamines before an allergic reaction has the chance to occur. Stay indoors during peak pollen hours, and take a shower immediately after being outside.
- Use PPE viz dust mask, other respirator.
- Keep wet the floorto prevent dust emissions
Fever due to inhalation
 |
| Occupational illness - Fever due to inhalation |
Inhalation fever includes polymeric fever and
metallic fever.
Polymeric smoke fever
It is inhalation fever and symptoms resemble the flu
and include fever, cough, and chest pain or tightness.
Cause: Smoke inhalation, which is emitted when
polytetrafluoroethylene is heated at high temperatures.
Preventive measures: Use appropriate
PPEs as half cartridge mask, coverall, ensure adequate ventilation, etc
Metallic smoke fever
It is inhalation fever and the patient has
flu-like symptoms, such as fever, cough, and chest pain or tightness.
Cause: Inhalation of smoke that contains certain
types of metal oxides, for example, zinc oxide and magnesium oxide, or by the
inhalation of smoke that occurs when heating or melting metals.
Source of exposure: Welding work,
workshop and foundry.
Preventive measures: Use
respirator protection, ensure adequate ventilation in welding area, Air blower
must be used in confined area, etc
Bronchopulmonary Diseases - Byssinosis
Byssinosis disease is associated with exposure to
cotton dust with both acute & long term effects. It is typically
characterised by asthma-like symptoms but can lead to irreversible reductions
in lung function because of narrowed airways and lung scarring. Symptoms
include difficulty breathing, cough and airway obstruction. Symptoms usually
appear on the first day of the work week and disappear on the following days.
If a worker is exposed to cotton cloth for a long time, his symptoms may become
chronic.
Cause: Inhalation
of Cotton dust
Source of exposure: an
untreated cotton cloth, manual cotton handling, textile mill, etc
Preventive measures: Controlling
dust is the best way to prevent byssinosis, Use dust mask, ensure adequate ventilation
at indoor area.
Occupational illness - Irritation
Occupational irritation may be to the eyes and airways
that exposed to gas or smoke based on its solubility. Very high or continuous
exposure to a hazardous substance may result in the involvement of the smallest
airways, causing inflammation and edema in the bronchiolar and can be fatal if
not treated. Certain irritants can also cause permanent lung damage, especially
if the exposure is very high or common. Others can make people susceptible to
conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pneumonia.
Cause: Inhalation
of various types of dust, gases and soluble vapours such as ammonia, chlorine sulfur
dioxide and insoluble gases, such as phosgene. Nitric acid, fluoride and ozone
can also cause a late reaction.
Preventive measures: Usually,
if someone is exposed to an irritant, they will move away from the source, limiting
any damage
Occupational illness - Suffocation or Asphyxiation
Simple suffocators are inert gases or vapors such
as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane, which displace oxygen from
the air in high concentrations. Chemical choking agents include carbon
monoxide, which is combined with haemoglobin to prevent the supply of oxygen to
cells, and hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide, which interrupt breathing at
the cellular level.
Cause: Deficiency
of oxygen
Source of exposure: confined
spaces, Inert atmosphere, CO and HCN atmosphere
Preventive measures: Use
breathing apparatus, Ensure adequate ventilation, Ensure provision of air blowers
in confined space, monitor oxygen concentration frequently in confined spaces,
etc
Occupational illness - Asthma
Asthma is an
inflammation of the airways, a chronic condition characterized by periodic
inflammation of the bronchi and hardening of the surrounding muscles. Typical symptoms
include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and breathing problems.
Asthma can be divided into two categories:
occupational asthma and work-related asthma.
Occupational Asthma
Severe asthma
attacks can lead to hospitalization and be fatal. Occupational asthma is
usually triggered in those who already suffer from it, but anyone can develop
it.
During an asthma
attack, a person may experience wheezing, coughing, difficulty breathing, chest
tightness, rapid breathing, anxiety and panic, a pale, sweaty face, difficulty
speaking and blue lips or nails.
Cause: Deficiency of oxygen to
lungs due to exposure of chemicals such as isocyanates and acid anhydrides, as
well as biological materials such as flour powder and certain proteins and
allergens from laboratory animals such as the skin, urine, fur or saliva of
rats and mice.
Source
of exposure: Occupational
asthma is the result of prolonged exposure to respiratory sensitizers present
in the workplace or in the context of professional activities such as
spray paint, cleaning products or adhesives, etc. Isocyanates are
chemical substances that are often found in two-part paints, glues and
pesticides.
Preventive measures:The best way to prevent
occupational asthma is to eliminate the hazardous substance and replace it with
a less harmful one. But there are cases where it is impossible to eliminate a
danger. Exposure should be minimized through controls such as ventilation, work
rotation, proper handling procedures, proper maintenance and PPE.
Work-related Asthma
People with asthma have chronic inflammation of
the bronchi (respiratory tract). As a result, the bronchial walls swell, which
causes the bronchi to shrink, which can cause difficulty breathing. The muscles
around the airways also become irritable, so they contract, causing a sudden
worsening of symptoms in response to various stimuli, including exposures found
at work. Inflammation can also cause the mucous glands of the bronchi to
produce excessive sputum that further blocks the already narrow air passages.
If the treatment does not control inflammation, while causing acute attacks, it
can lead to permanent narrowing and healing of the airways.
Causes: Exposure to irritant gas, fume
or vapours.
Source of exposure: Irritants
generally occur within hours of exposure to high levels in the workplace.
Preventive
measures: The
best way to prevent work-related asthma is to eliminate the dangerous substance
and replace it with a less harmful one. But there are cases in which it is
impossible to eliminate a danger. Exposure should be minimized through controls
such as ventilation, work rotation, proper handling procedures, good
maintenance and PPE.
Occupational Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
Occupational allergic Alveolitis is the infection
of the alveoli by an allergen. Symptoms usually begin a few hours after
exposure, with flu-like symptoms: fever, fatigue, and chills. As the disease
progresses, the patient suffers from breathing difficulties and develops a
cough. Persistent exposure can cause chronic symptoms and fibrosis of the
lungs. The "farmer's lung" is a type of extrinsic allergic alveolitis
and is caused by inhaling dust or traces of moldy hay, grain or straw.
Cause: inhalation of organic dusts or
microbially contaminated aerosols
Source of exposure: arising
from work agricultural activities creating dust or spores arising from mouldy
hay, grain or straw.
Preventive measures: Use dust
masks, half/ full mask respirator, ensure adequate ventilation, monitor the concentration
of organic dust, elimination of antigen exposure antigen can be
identified, the most effective therapy is complete avoidance. Acute disease
remits without specific therapy.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases
caused by the inhalation of coal dust, quarry dust, wood dust, grain dust and
agricultural work, dust in stables, textile dust and paper dust, resulting from
'' professional activities
Occupational cancer
Cancer is abnormal growth of body cells. Cancer
can occur anywhere in the airways, from the nose to the lungs. Although the
main cause of lung cancer and other forms of respiratory cancer are the
hazardous substances present in some workplaces, they can also cause cancer,
for example, crystalline silica, diesel exhaust particles and radon
Asbestos exposure can cause lung or mesothelioma
cancer, cancer of the lining of the lungs or intestine. Relatively low levels or
short-term exposure to asbestos can cause both types of cancer.
Causes: ageing, exposure to radiation,
chemicals and other substances at work and in the environment, family history
of cancer, and many behaviours and lifestyle factors such as tobacco smoking,
poor diet, lack of physical activities and being overweight. If employees are
exposed to asbestos and also smoke, they have a much higher risk of developing
lung cancer than those who are exposed or only smoke asbestos.
Source of exposure: People
who are generally exposed to asbestos in plumbing work, carpentry work and
other work in the construction and maintenance of buildings. People exposed to
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as coca workers, have an increased risk
of lung cancer. Other lung carcinogens are arsenic.
Mesothelioma | Asbestos Cancer to Respiratory system
Mesothelioma is a form of cancer that takes
several years to develop after inhaling asbestos fibers, but which is usually
fatal after the onset of symptoms. It mainly affects the pleura (the outer
lining of the lungs) and the peritoneum (the lining of the lower digestive
tract). Many cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage because the symptoms are
generally non-specific and appear late in the development of the disease. It is
almost always fatal and often within twelve months of the onset of symptoms.
Occupational Skin diseases
Skin diseases caused by exposure to allergens or
irritants Occupations with the highest rates are florists, beauticians, chefs,
hairdressers and barbers, and certain occupations related to manufacturing and
health care. Other conditions reported in EPIDERM include contact urticaria,
folliculitis, acne, infectious and mechanical skin diseases and skin cancer.
Work-related skin diseases include any skin
disorder caused or aggravated by work or professional activity.
"Professional" skin conditions are generally reserved for cases
caused directly by work.
The severity of professional skin disease can vary
widely, from severe cases of dermatitis to mild skin irritations, which the
individual may not recognize as an adverse health effect.
The term "occupational" skin disease is
generally reserved for cases that are directly caused by work.
Allergic contact dermatoses Contact
with soaps and cleaning products and working with wet hands are still the most
common causes of occupational dermatitis. Other common causative agents are
"chemicals and rubber materials", "personal protective
equipment" (including latex gloves), "preservatives",
"bleaches and sterilizers" and "nickel".
Dermatitis is the inflammation of the upper layer
of the skin. Dermatitis causes the skin to break out in rashes that burn or
itch. The skin can become inflamed, itchy, blisters, cracks and dryness.
Occupational dermatitis most often affects the
hands and forearms. Indeed, the substances that cause dermatitis generally come
into contact with these areas.
Cause: soaps, detergents, cleaning chemicals, and flour. Frequent sashing of hands
can also cause contact dermatitis.
Irritant contact dermatoses caused
by other recognized irritant agents occurring from work activities.
Cause: contact with irritants
include soil, meat, fish, poultry, citrus fruits, dough, spices, herbs,
and sugar.
Preventive measure: Gloves can reduce exposure and prevent dermatitis. However, some
people are sensitive to latex and rubber and may need cotton or hypoallergenic
gloves. To reduce exposure, job rotation may be the best option.
Occupational Musculoskeletal Disorders
Musculoskeletal
disorder is a muscle and joint problem that affects the ability to work and
live well. It includes, for example, various types of stress, sprains and
excessive use. back problems, slipping discs and work-related problems in the
upper limbs. Other symptoms vary depending on the person, such as pain,
numbness, stiffness, swelling, and tingling.
They can be episodic
or chronic and can also be the result of injuries during a work accident.
Moreover, they can develop from mild to severe disorders. These disorders are
rarely life threatening, but affect the quality of life of a large proportion
of the adult population. Work-related disorders can develop in a work
environment due to the physical tasks with which people perform their normal
work activities.
WRMSDs are
associated with working models that include:
- Fixed or limited body positions
- Continuous repetition of movements.
- Strength concentrated in small parts of the body, such as the hand or wrist.
- A work pace that allows insufficient recovery between movements. In addition, psychosocial factors in the workplace, such as organizational culture, health and safety climate and human factors, can create the conditions for WRMSD to occur.
- Patients who present WRMSD to their GP suggest that most suffer from back pain or hand, wrist or arm problems. This may be due to repetitive movements and probably reflects what is suggested in the Labor Force Survey.
Here are the types
of musculoskeletal disorders.
Radial styloid tenosynovitis related to
repetitive movements, vigorous actions and severe postures of the wrist.
Olecranon bursitis related
to protracted pressure on elbow region.
Prepatellar bursitis related
to extended stay in kneeling posture.
Epicondylitis related to repetitive strong
work.
Meniscus lesions subsequent prolonged periods
of work on knee or squat posture.
Carpal tunnel syndrome related
to prolonged periods of repetitive vigorous work, vibration work, severe positions
of the wrist, etc
Hand arm vibration:
Exposure to vibration
due to power tools may cause Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS). Hand-Arm
Vibration Syndrome consist of two components: Vibration White Finger and
sensorineural effects.
Causes: The causes of common musculoskeletal problems are:
- Lifting heavy or awkward loads.
- Repetitive activities such as packing and
stacking.
- Sitting in awkward positions for prolonged
periods.
Preventive
measures: Numerous
health and safety practices reduce the risk of Musculoskeletal disorder. Consider
the assistance of mechanical aid or another person. If the job involves manual
lifting, reduce weight where possible and distribute it evenly while carrying.
Break repetitive tasks performing repetitive tasks. Change keyboard monitor or
mouse layout to resolve the problems of wrists and neck pain. Changes in chair or desk can be considered to
accommodate height. Avoid positioning of yourself uncomfortably as this places
strain on your body.
Mental and behavioural disorders
Stress is harmful reaction that people have pressures
and requirements placed on them at work. Stress at work is psychosocial factors
and is related with common conditions such as heart disease, anxiety, depression
and may associated with musculoskeletal disorders.
Other
mental or behavioral disorders can be determined scientifically or by methods
appropriate to national circumstances and practices, between exposure to risk
factors resulting from professional activities and mental and behavioral
disorders developed through work.
Work-related
stress and mental health problems are responses to significant levels of
pressure and long-term demand in the workplace, especially when this demand
exceeds its capacity. It compromises your ability to cope and causes a
deterioration in your mental state. Chronic stress influences work and health
in general and can lead to depression.
Chronic
work-related stress causes physical and mental disorders, such as skin
problems, chest pain, headache, nausea or dizziness, panic attacks, difficulty
concentrating, high blood pressure, frequent colds, fatigue, apathy Forgetting
to become too emotional, aggressive / negative, refuses to listen to advice /
requests. and withdraws
Unlike
other diseases, the causes of work stress are more abstract and are not limited
to one or two specific professions. Work stress is caused by too many or too
few demands, lack of control, lack of support, bad relationships, their role. ,
organizational changes at work, violence and insecurity of roles, that is,
uncertainty about work / insecurity about what to do.
Preventive
measure
- Take short breaks during the day.
- Use holiday pay.
- Ensure a clear separation between home and work.
- Determine habits at the end of the day, such as making a list of things you can do tomorrow.
- Ask for help.
- Improved time management skills.
Create a general
culture of effective stress response prevention without incurring secondary
costs due to the side effects of medication, medication costs, lost work days
and with clear benefits in terms of work efficiency and balance between work
and life. Moreover, these interventions do not generate a stigmatizing response
in the entire system, because "they are not psychiatric," even if they
are deeply rooted in life and psychological balance.
Stress measurement
can be performed using the stress measurement instrument and therefore an
action plan for reduction can be developed. There are other tools to prevent
the stress level of employees. Yoga and light exercises. Yoga focuses on
empowerment and self-efficacy, works at body level to influence the mind-body
system and promotes a central role for employees in the search for health and
balance in daily life.
There is sufficient
evidence to support the hypothesis that the introduction of large-scale yoga in
the workplace and meditation will benefit both employees and the performance of
teams and organizations.
Some people are not
in favor of yoga because of their perception that it is not practical, philosophical,
esoteric, religious, and at least as something related to personal life and
personal choices.
To overcome these
prejudices, yoga teachers must develop the skills to introduce yoga and give
yoga classes in profan language, with scientific evidence of the benefits of
yoga.
Note: Some time mental stress may due to STDs or STIs which most of the peoples are don't comfortable to share with their partners, most of the symptoms of STD are not visible, to learn more and to test confidentially, you can find detail information in below link.
Occupational Diseases Noise
Noise is defined as "unwanted sounds,"
while sound is a term used to describe the sensation the brain receives when
the ear detects changes in air pressure. The higher the noise level and the
more people are exposed to it, the greater the risk of damage.
The effects can cause temporary or permanent
hearing damage and affect the effectiveness of employees. People with hearing
problems, whether due to their age or illness, can make their problems worse by
being exposed to higher noise levels at work. It can also cause accidents due
to limited voice communication, misunderstandings about verbal instructions and
masking sounds of imminent danger or warnings.
Main sources of noise at work
- Use of heavy machinery
- Vehicle movement in workplace
- Use of power tools such as circular saws and cutting heads.
- Production lines
- Use of pneumatic tools such as drills, grinders and staplers
- Use of electric motors and generators
- Engineering processes such as metal production.
- Factory facilities where ventilation equipment must operate continuously.
Dangerous noise levels
Noise levels above 75-80 dB (A) cause hearing
damage.Noise level of 85 dB (A) may take eight hours to damage hearing, while
noise of 100 dB (A) can damage the hair cells in the ear after 30 minutes.
Symptoms of hearing loss
- Ringing in the ears
- Inability to hear soft and high pitched sounds
- Speech and other sound damping
- Difficulty understanding conversations from a distance or in a crowd
- Difficult to determine from which direction the sound comes
- Feel tired or stressed regularly because you have to concentrate while listening
- Inappropriate responses or responses in conversations
- Read lips or see people's faces with more attention during conversations
- Feel nervous about listening and understanding others.
It takes ten years from the moment someone
realizes they have a hearing loss before doing something.
Effects of noise on health
Health effects can be caused by a single exposure
to very loud noise or by exposure to high noise levels over a longer period.
The effects of noise on hearing depend on:
- Sound intensity or pressure
- Frequency or tone
- Exposure time
- Distance to the source
- Individual sensitivity
- Other factors (lifestyle, age, illness, genetics, etc.).
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is the first sign
of hearing damage. Extreme exposure to noise surges the risk of tinnitus. If
the sound is impulsive, the risk can increase considerably. Tinnitus can be a
very painful condition and can lead to sleep disorders and unclear speech.
There is no effective cure for this condition, but there is treatment to
relieve the symptoms.
The permanent threshold change occurs when people
are regularly exposed to high noise levels for a long time. It also occurs with
repeated exposure to noise without sufficient time between exposures to allow
normal hearing recovery, resulting in permanent hearing damage. Hearing loss
can have a significant impact on a person's personal and professional life.
Effect on pregnancy
Exposing pregnant workers to high noise levels can
affect the fetus. Research suggests that the long-term exposure of the fetus to
high noise levels during pregnancy may have an effect on the child's subsequent
hearing and that low frequencies have a greater potential to cause damage.
Physiological effects
Noise can affect the cardiovascular system, causing
an increase in blood pressure and the release of catecholamines in the blood.
An increase in the level of catecholamines in the blood is associated with
stress.
Professional stress
Work stress rarely has a single cause and often
results from the interaction of several risk factors. Persistent noise in the
work environment can be stressful, even at low levels.
Other effects
Excessive noise levels may increase the risk of
unwanted events or incidents by:
- Distract employees, such as drivers
- Make it difficult for employees to hear and understand instructions correctly
- Mask imminent danger noise and warning signs
- Contribute to irritation and discomfort that can lead to human errors.
An individual's performance on tasks that require
constant attention (critical safety tasks) can be affected by noise, as it can
distract them, resulting in poor judgment and decision-making processes.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
 |
| Occupation-health-diseases-noise |
Cause: If a sound exceeds 85 decibels,
prolonged exposure will cause permanent hearing loss. Working in an environment
where noise approximately 95 decibels without adequate safety measures or
without the use of PPE, can cause NIHL.
Preventive
measures: Wear PPE such as earmuffs, install
noise control devices, follow the work methods.
You may find affiliate links in this article. This means that if you click on a link and purchase any of the products on this page, we may receive a commission, at no additional cost to you, It does not affect our knowledge sharing, opinions or reviews. Everything we do is benefit for you as the reader, so all our knowledge sharing, reviews are as honest and unbiased as possible.
Conclusion
Occupational ill-health is a chronic disease caused by repeated exposure to work hazard during
performing routine work activities. It has multiple causes including work environment together with other risk
factors.
Occupation diseases may be occurring individually or among a group of exposed people
and develops over time. Prevention is
only option to treat with occupational diseases. Improvement in ergonomic work environment
and changes in lifestyle may help to prevent occupational illness.
You may find affiliate
links in this article. This means that if you click on a link and purchase any
of the products on this page, we may receive a commission, at no additional
cost to you, It does not affect our knowledge sharing, opinions or reviews. Everything
we do is benefit for you as the reader, so all our knowledge sharing, reviews
are as honest and unbiased as possible.








That's very Informative blog...
ReplyDeletehealth and safety preventative measures
Easily, the article is actually the best topic on this registry related issue. I fit in with your conclusions and will eagerly look forward to your next updates. bible nutrition
ReplyDeleteEarned health is not determined or advanced by medical interventions. Static health, that is, health along the continuum from the center to the left of the of the continuum, is so influenced. hasta yatağı
ReplyDeletedf
ReplyDelete